How Garage Doors Work
Ever wondered what goes on behind the scenes every time you hit that garage door opener? This comprehensive guide demystifies how your garage door system works. From the mechanics of the door itself to the electrical and safety features that keep it operating smoothly, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of this essential home feature.
By: Kelly Larson | Published: April 4, 2025
Find Garage Door Repair Services
Get a fast & free quote | Schedule your service today
It’s easy to take your garage door system for granted. You push the button and the door goes up. You push it again and the door goes down. Simple, right? But in order to make that happen, dozens of mechanical, electrical and safety components need to work together in perfect harmony behind the scenes.
Having a working knowledge of the many garage door mechanics in play helps you perform routine maintenance and troubleshoot potential issues with the system. By walking through your garage door’s primary components and their unique functions, our guide demystifies the inner workings of one of your home’s main entry point.
The Basic Components of a Garage Door System
Standard residential garage door systems include the door panels, opener, tracks, rollers, springs, hardware and any advanced smart-home features. If one part fails, the entire system can fail. Before getting into the spring system and garage door opener, we’ll start with the door itself and the non-motorized components that allow it to seamlessly open and close.
The Door Panel Structure
Garage door panels wear many hats. They provide insulation, weatherproofing, safety from intrusion and other key functions. They’re available in a variety of materials with varying levels of insulation. Most of them are made up of individual panels joined together by brackets to form the door. Heavier doors—wood, for example—require stronger springs and a powerful opener to lift them.
Steel panels are a popular choice thanks to their durability, low price point and low maintenance requirements. Aluminum doors are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them a common material for coastal areas. Wood and fiberglass panels are less common but offer strong resistance to the elements and excellent curb appeal.
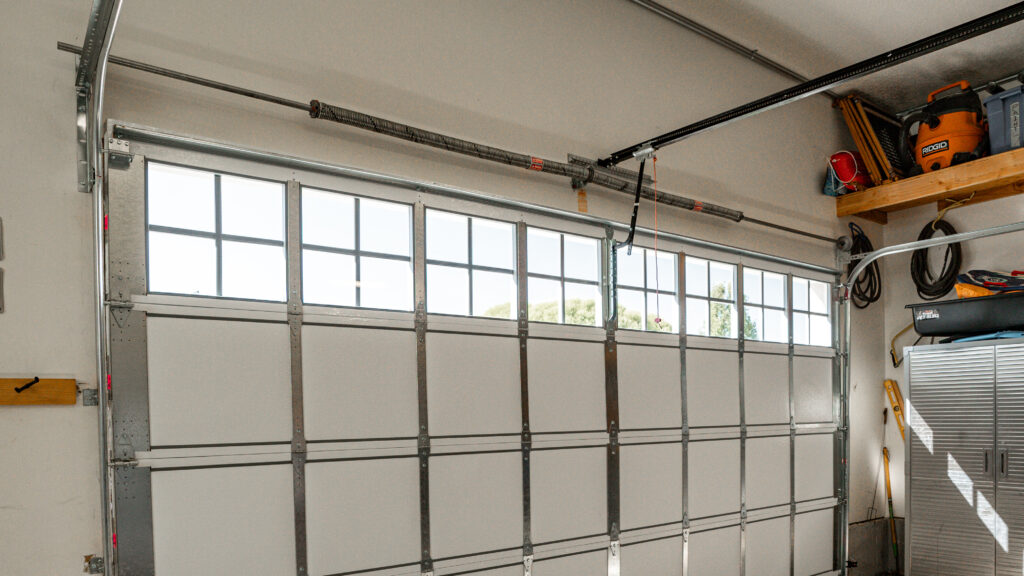
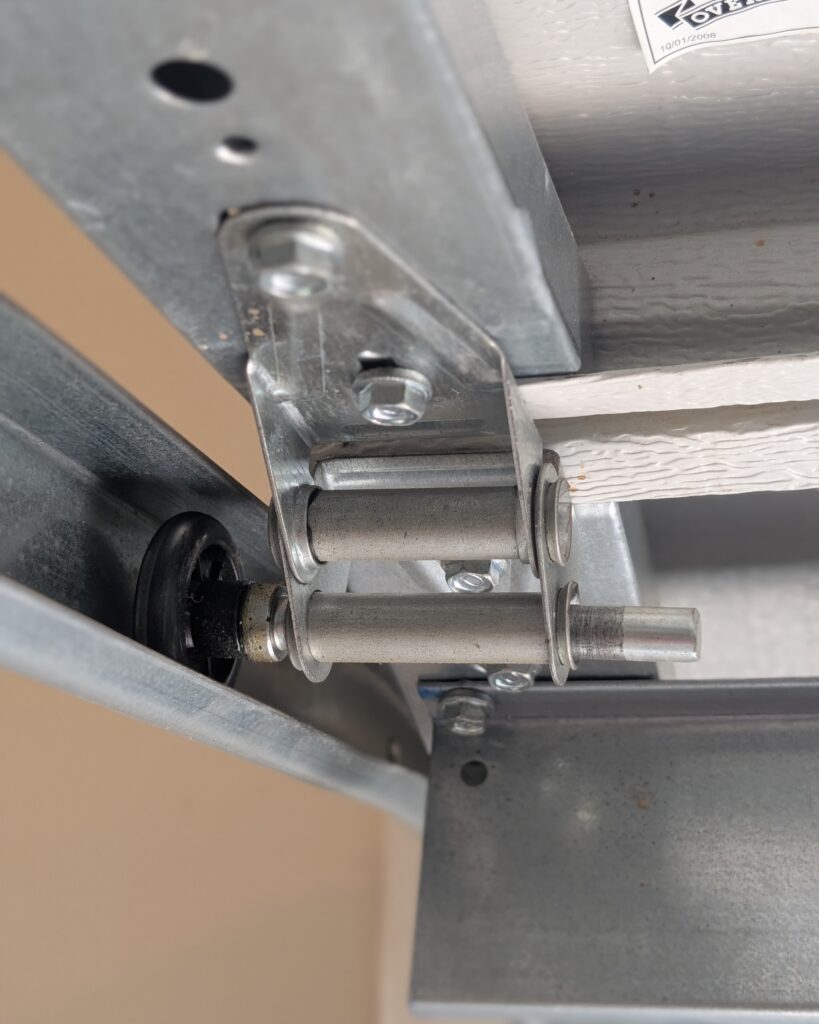
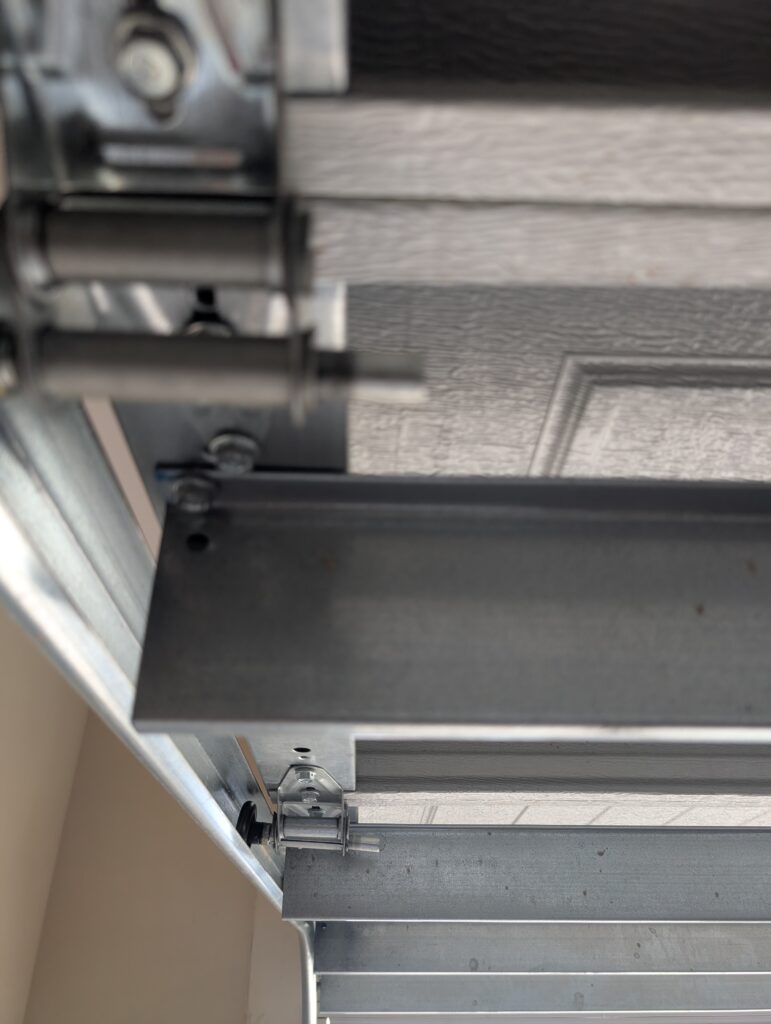
Tracks, Rollers, and Hardware
The track system and its rollers guide the door up and down, and hinges and brackets keep everything together.
- Track System: Garage door tracks are metal pathways mounted to the frame of the garage door. They guide the door first vertically, then horizontally until it’s fully open.
- Rollers: The rollers are mounted on the sides of the garage door and fit into the tracks. They play a crucial role in reducing friction and noise, and are typically made of steel, nylon or plastic.
- Hardware: Hinges connect the panels of the door together. Brackets, located at the top and bottom of the door, support the tracks and keep them stable. Other hardware like nuts, bolts and fasteners keep the whole system in place.
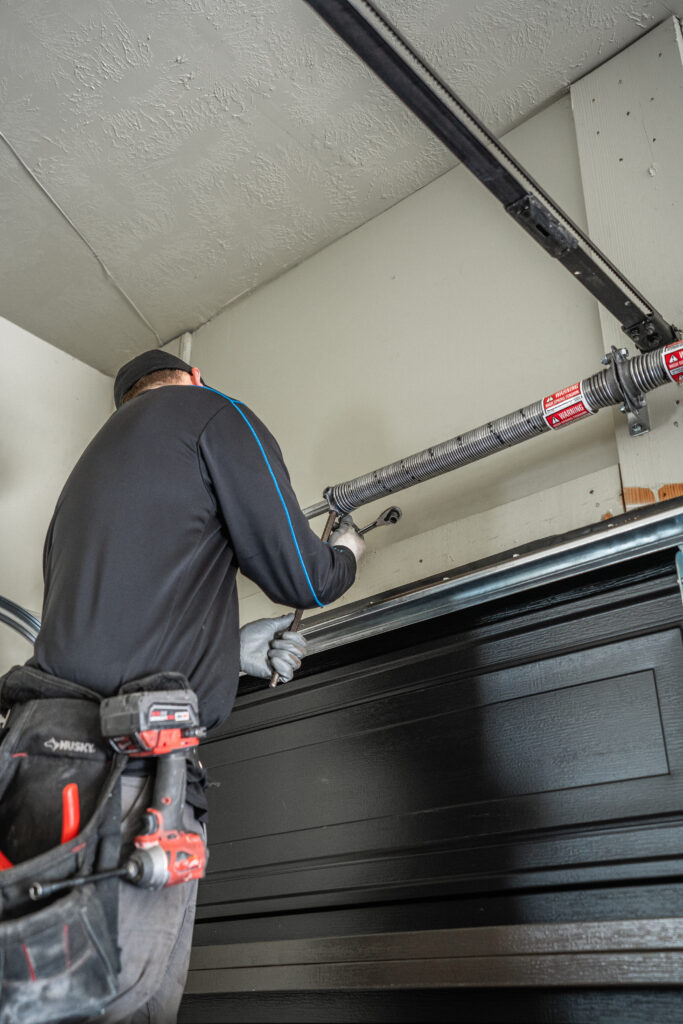
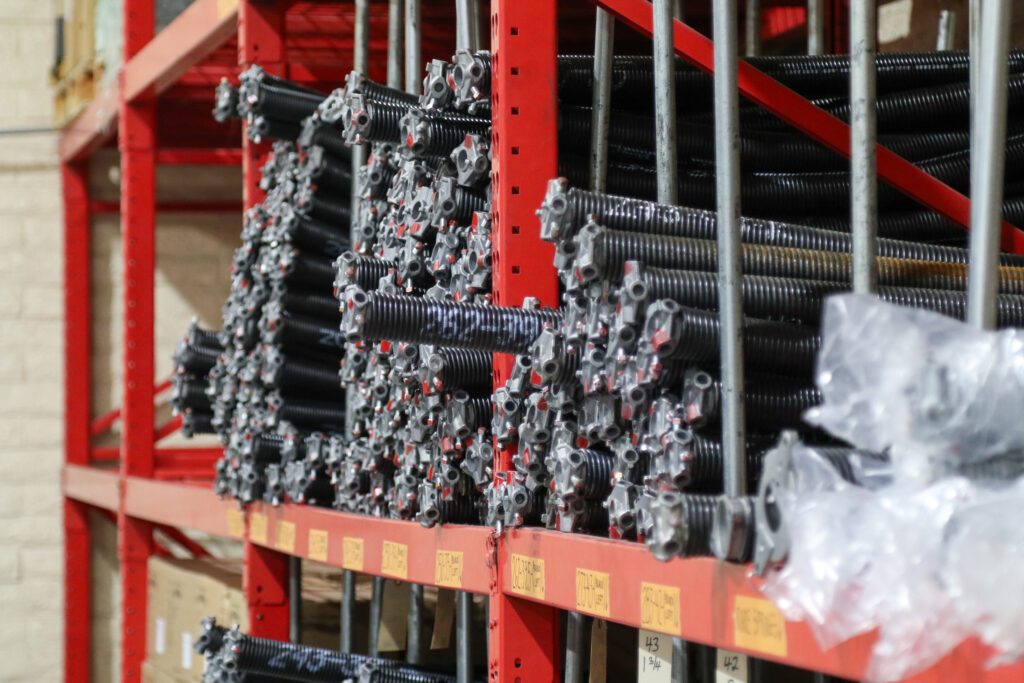
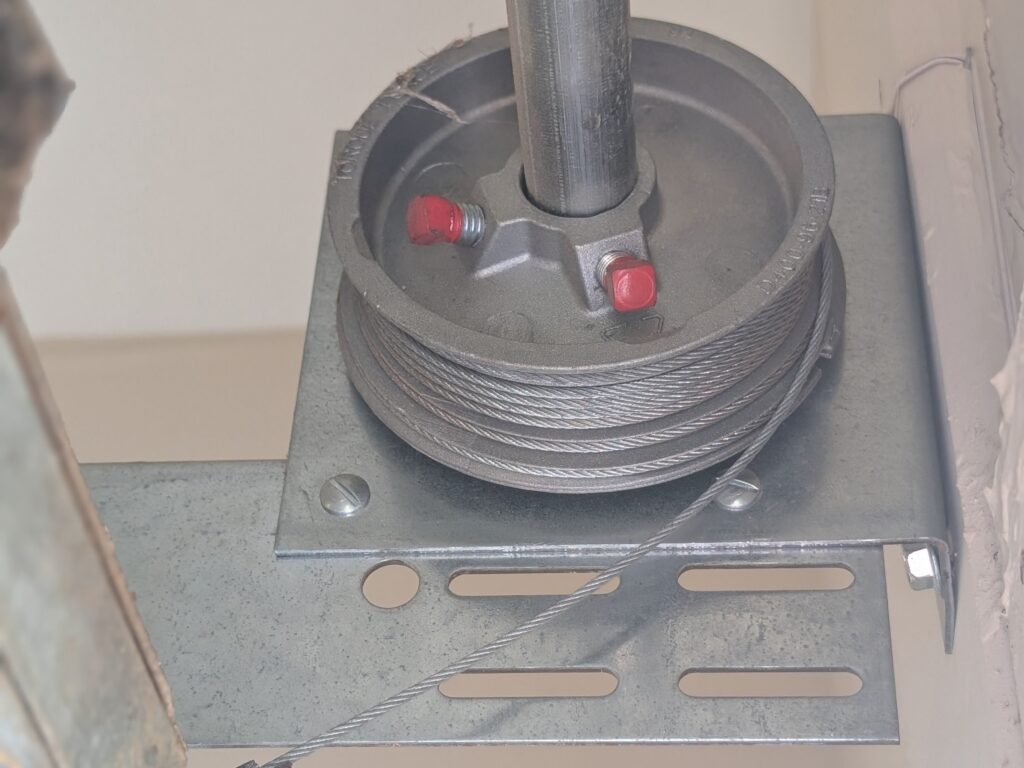
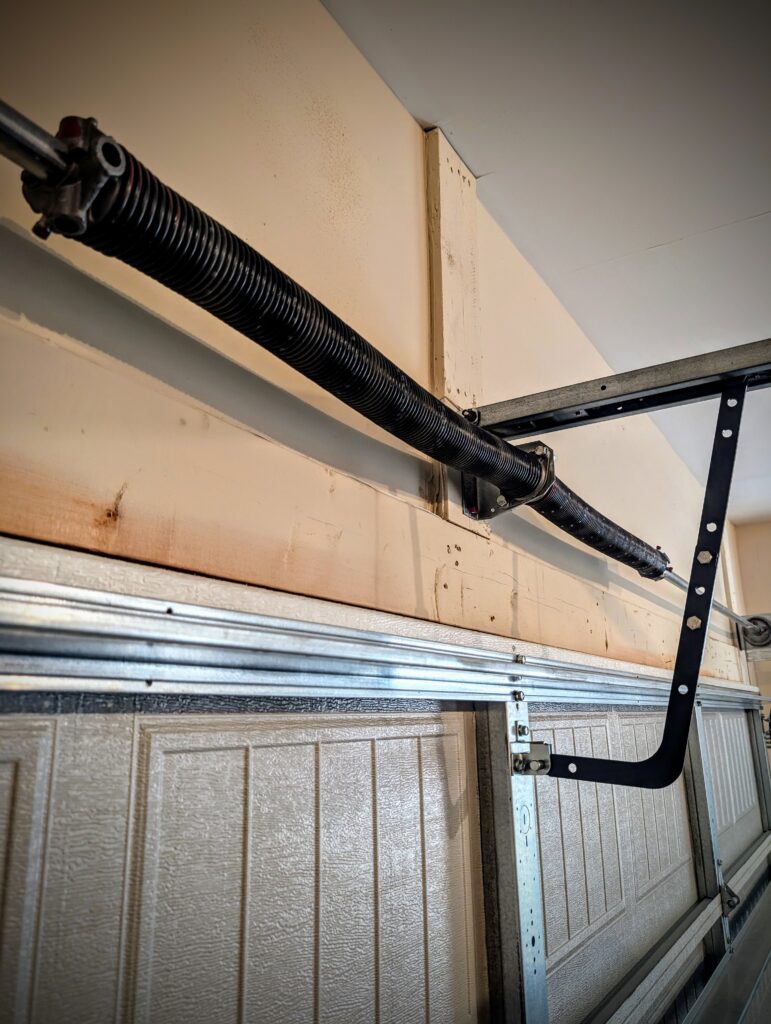
Understanding Garage Door Springs: The Power Behind Your Door
Garage door springs are the workhorses of the system, and their are two main types: torsion springs and extension springs. They both counterbalance the weight of the door with stored energy, and without them, the opener’s motor wouldn’t have enough power to open and close it. Given the extreme amount of force that garage door springs hold, we highly recommend hiring a professional to for installation and repairs. Garage.com can help you find a licensed professional in your area.
How Torsion Springs Work
Torsion springs are mounted above the garage door and store a significant amount of rotational force, or torque. When the door opens, the springs unwind. When it closes, they wind back up to their original position. Torsion springs provide a stronger counterbalance than extension springs which results in less overall strain on the garage door system’s components.
Extension Springs Explained
Unlike torsion springs, extension springs are located on either side of the garage door. To counterbalance the weight of the door, they extend as it opens and retract as it closes. Extension springs have a less complicated design than torsion springs. While this makes them a better candidate for DIY installation and repairs, you should still exercise extreme caution if you decide to go that route.
Since they’re under significant pressure, extension springs are very dangerous if they break. To help prevent injury, safety cables are installed through the center of the springs and attached to a support on either side. If a spring breaks, the safety cable catches it and keeps it from becoming a projectile.
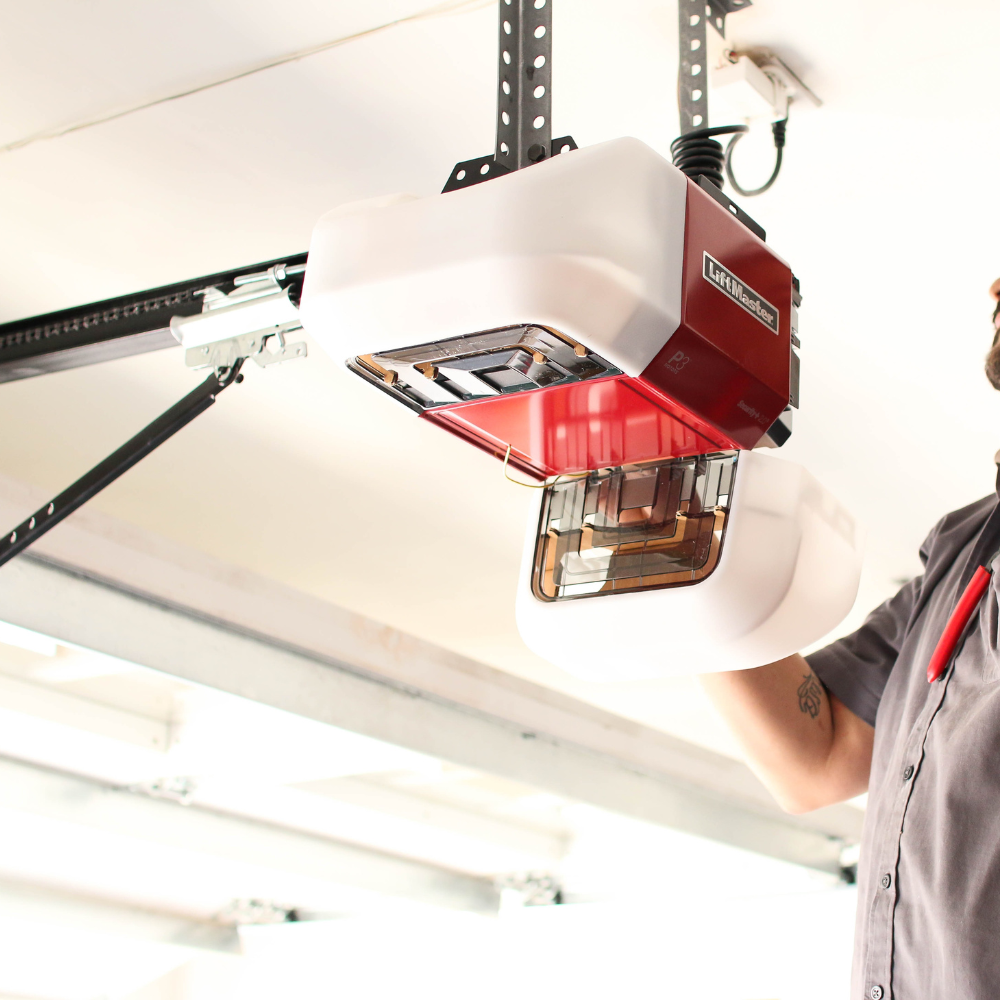
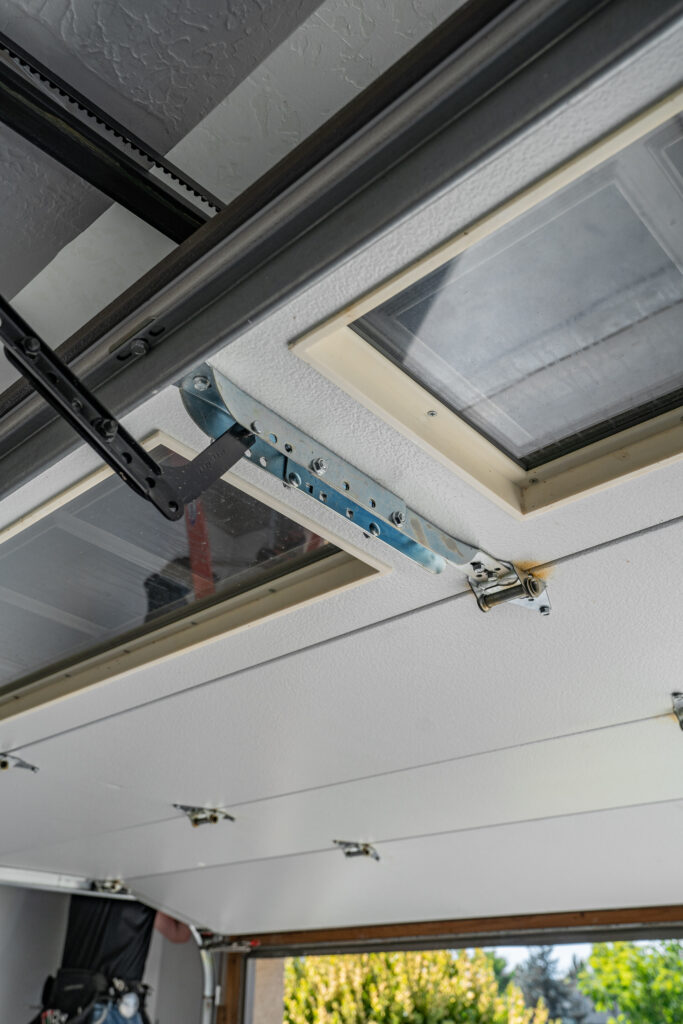
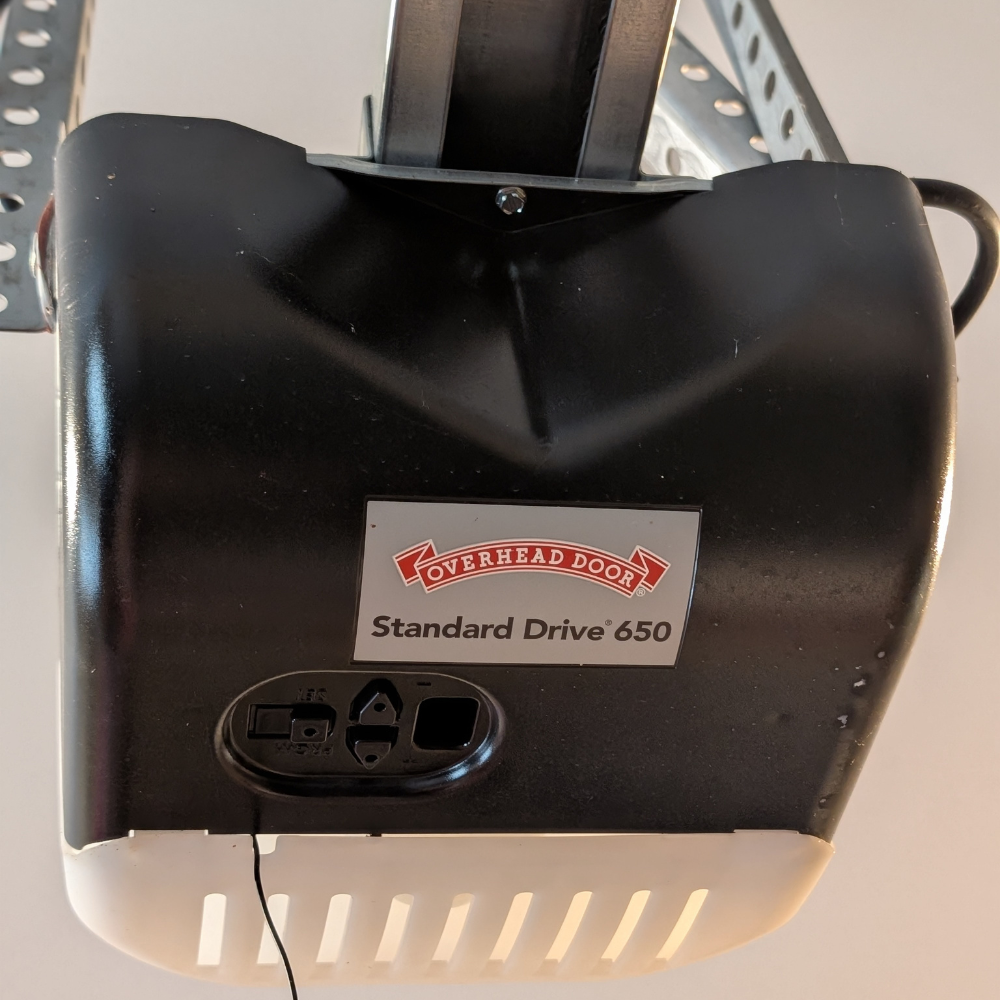
The Garage Door Opener System
The garage door opener typically hangs from the center of the garage ceiling and comprises a motor, drive mechanism, remote control system and any included safety and smart features.
Motor and Drive Mechanisms
The motor provides power to the garage door opener. Most residential motors are electric, but homeowners can also upgrade to a hydraulic or pneumatic unit. How much horsepower your motor has affects its performance and how heavy of a door it can lift. Generally, ½ HP is adequate for lightweight and smaller doors, ¾ HP is standard for two-door garages and motors with 1HP and above are best suited for commercial units or heavier residential doors.
The garage door opener’s drive mechanism connects the motor to the door itself. The most common drive mechanisms are chain drives and belt drives. Screw drives, direct drives and jackshaft units are also available but are less common.
- Chain drive: Uses a metal chain to lift and lower the door. It’s the most common and cost-effective drive mechanism, but they’re loud and require frequent maintenance.
- Belt drive: A steel-reinforced rubber belt that powers the door. Though they’re more expensive, belt drives are quieter than chain drives.
- Screw drive: Uses a threaded steel rod that acts like a screw to power the door’s movement.
- Direct drive: Instead of the chain moving through the motor, direct drive units have a stationary chain that the motor moves across.
- Jackshaft: Quiet, space-saving units that use torsion tubes to move the door. Instead of hanging from the ceiling, they’re located on the side of the garage door. Most suitable for commercial or heavier residential garage doors.
Smart Technology and Modern Features
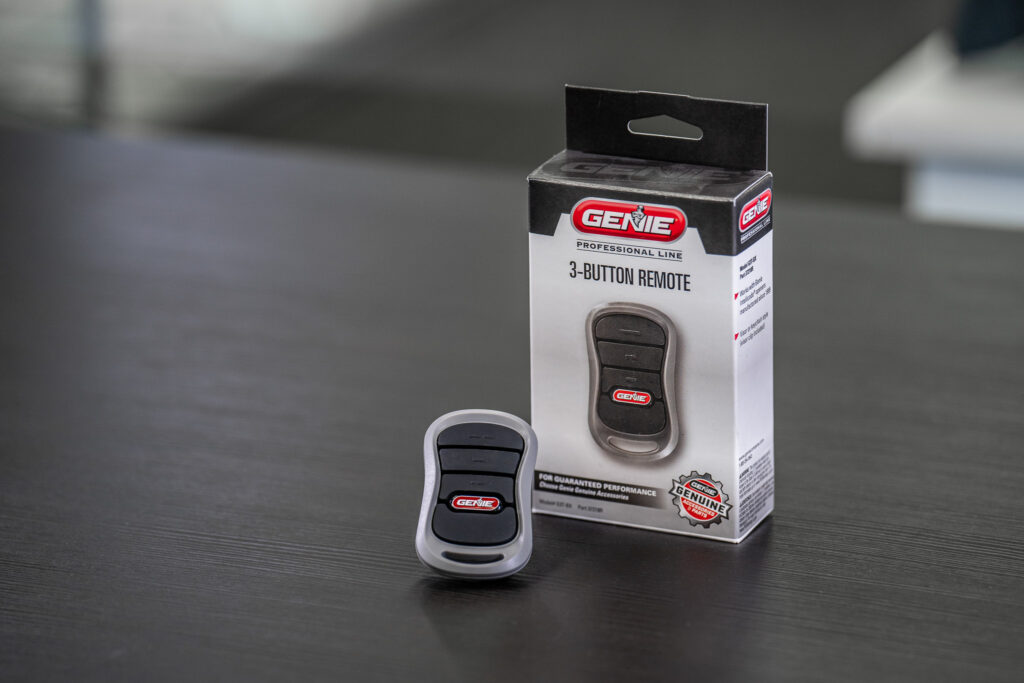
Over the years, garage door openers have evolved to include advanced smart tech and connectivity with your home’s safety and security systems. If features like this are important to you, look for an opener that’s compatible with platforms like Google Home, Amazon Alexa or Apple HomeKit.
Battery backup systems, which allow the opener to remain functional during power outages, are also widely available. Some units allow for remote access from your smartphone via a corresponding app, and security features like rolling code technology generates a new code each time the door is opened.
How Your Garage Opens and Closes
When you press the button on the wall or your remote, an electrical signal is sent to the garage door opener to activate the motor and begin the opening process. From there:
- The drive system engages: Whether through a chain, belt, screw, direct or jackshaft drive mechanism, the motor then provides enough power to move the door up and across the vertical and horizontal tracks.
- Springs hop in with the assist: The torsion or extension springs provide counterbalance, giving the motor much-needed assistance to move the door. They store energy when the door is closed and release it as it opens.
- The opening cycle ends: Once the door is fully open and the springs are extended, the motor shuts off and waits for the next signal. When you push the button to close the door, the same process happens in reverse.
The Safety System in Action
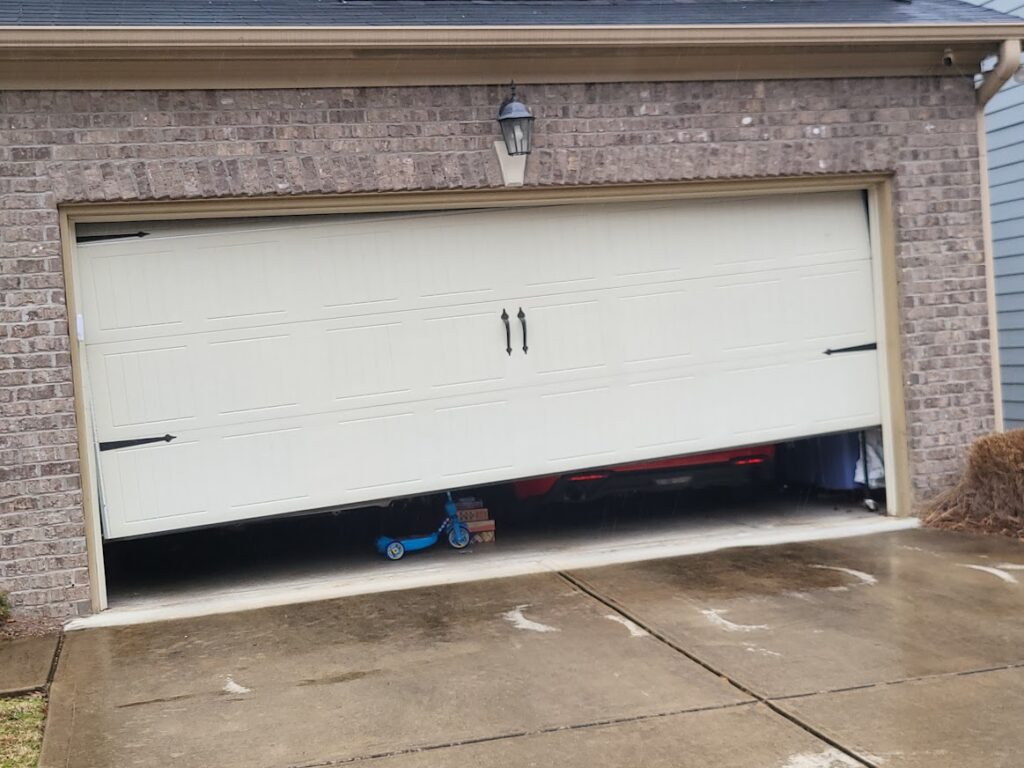
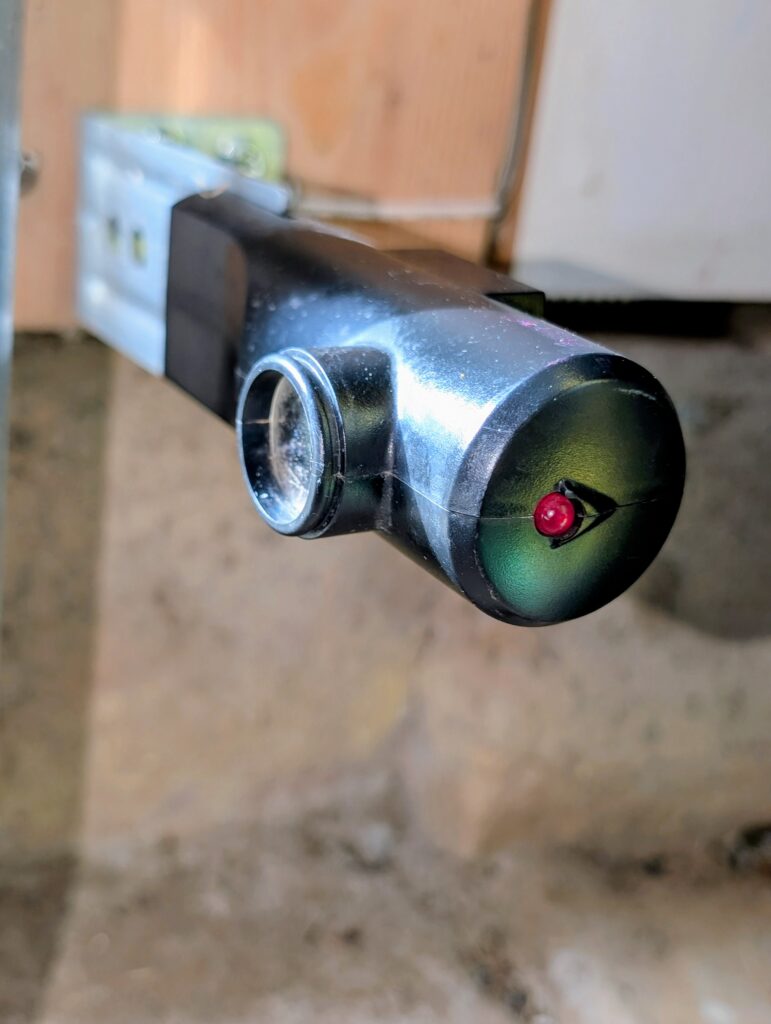
Garage door sensors help prevent accidents by stopping or raising the door if an obstruction is detected, most commonly by an infrared beam. They became mandatory in 1993 under a rule published by the Consumer Product Safety Commission. There are three main types of safety sensors:
- Infrared sensors: Two units are attached to either side of the garage door. One emits an infrared beam and the other detects it. When the beam is interrupted by even the slightest obstruction, it automatically signals the garage door to reverse.
- Pressure sensors: Often used as a backup to infrared sensors, they attach to the bottom or sides of the door and reverse its course if resistance is detected.
- Carbon dioxide sensors: CO2 can be deadly if it reaches a certain level in your garage. A CO2 sensor automatically raises the garage door if it detects a dangerous amount of the gas.
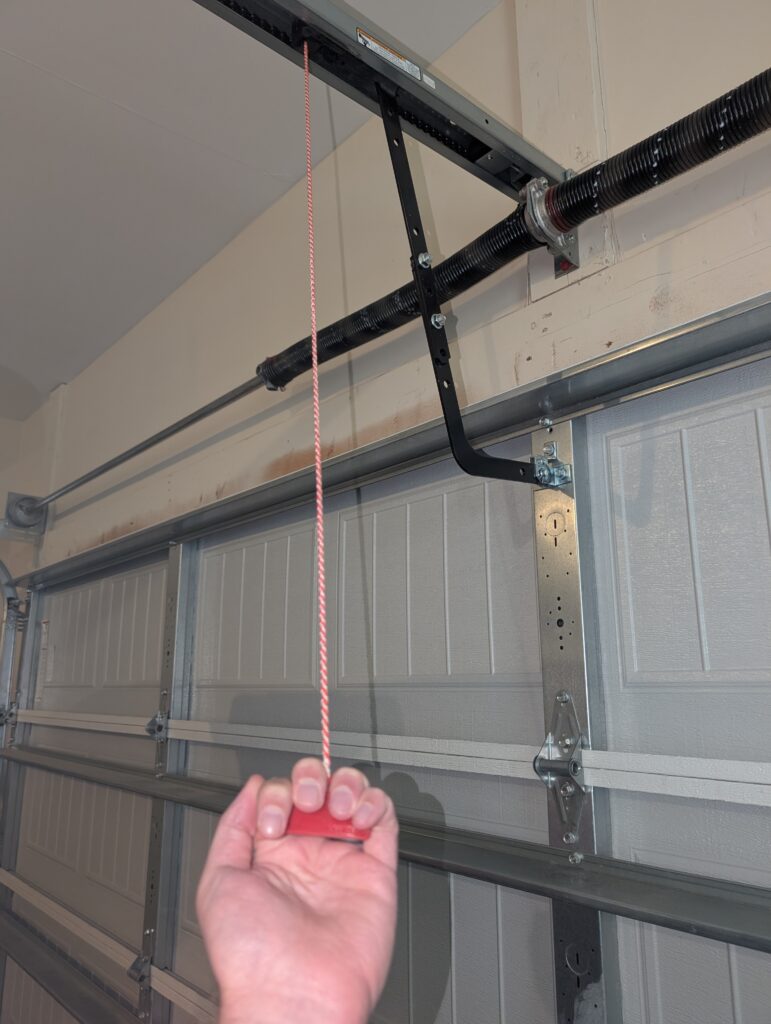
If you lose power, you can still raise and lower the door by pulling on the manual release cord. It’s often red and typically hangs from the trolley that connects the door arm to the drive mechanism. Pulling it disengages the motor from the door and allows you to manually open and close it. The springs will still provide enough counterbalance even when the motor isn’t working.
Maintenance Tips to Keep Your Garage Door System Running Smoothly
Proper ongoing maintenance will increase the longevity and efficiency of your garage door system. Check the manufacturer’s instructions for each of the components you’re working on. Some common ongoing repairs include:
- Lubricating moving parts
- Inspecting safety sensors for dirt and debris or misalignment
- Examining cables and hardware
- Cleaning the tracks
- Replacing seals and weatherstripping components
If the door is unresponsive, making unusual noises or not operating properly in other ways, consider contacting a professional to determine whether a part should be repaired or replaced. And never conduct DIY repairs or replacements to dangerous parts like springs and entire doors.
Frequently Asked Questions About Garage Door Operation

Get Your Free Quote and Schedule Your Garage Repair Today
Find top-rated companies for fast garage repairs and service to make sure your garage door system lasts. Get free quotes from garage door companies in your area.
Tips and Expert Advice for Your Garage
Stay informed with expert advice on garage door maintenance, garage door service, garage door replacement, and upgrades. Explore our blog for guides, troubleshooting tips, and more.